L’Insertion Sort è un Algoritmo di ordinamento (utile per i dataset quasi ordinati) che considera ogni elemento uno alla volta e li inserisce nella posizione corretta rispetto agli elementi già ordinati.
- Ad ogni passo, l’elemento corrente viene confrontato con gli elementi precedenti fino a quando viene trovata la sua posizione corretta.
- Solo alla fine dell’ultima iterazione gli elementi saranno nel loro ordine corretto.
Input: una sequenza di
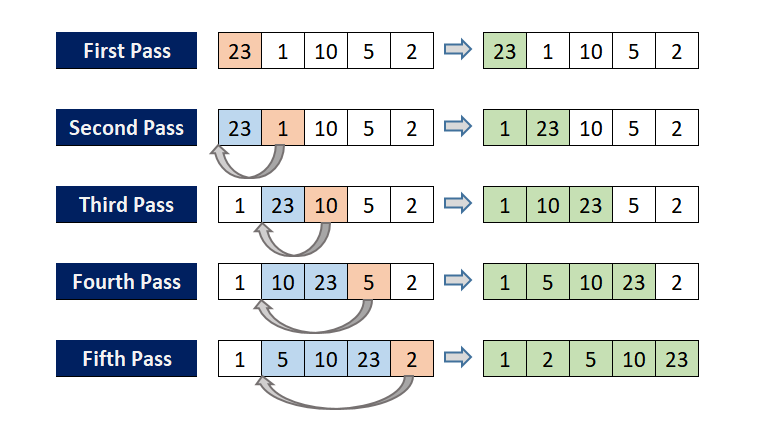
Caratteristiche
- Stabile: Naturalmente stabile.
- In-place perché l’ordinamento viene effettuato in input.
- Complessità di Tempo:
| Nome | Caso migliore | Caso medio | Caso peggiore |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion Sort 1 | |||
| Insertion Sort 2 | |||
| Insertion Sort 3 |
Codice
def insertionSort(arr):
n = len(arr) # Get the length of the array
if n <= 1:
return # If the array has 0 or 1 element, it is already sorted, so return
for i in range(1, n): # Iterate over the array starting from the second element
key = arr[i] # Store the current element as the key to be inserted in the right position
j = i-1
while j >= 0 and key < arr[j]: # Move elements greater than key one position ahead
arr[j+1] = arr[j] # Shift elements to the right
j -= 1
arr[j+1] = key # Insert the key in the correct position
# Sorting the array [12, 11, 13, 5, 6] using insertionSort
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
insertionSort(arr)
print(arr)